Appellations
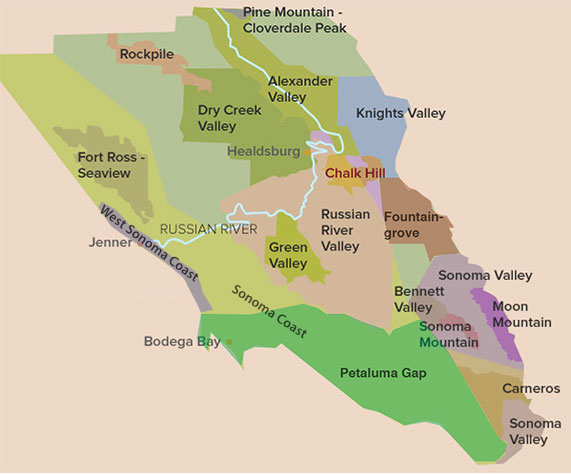
Chalk Hill Appellation (AVA)
1,400 vineyard acres
4 wineries
Earned AVA status in 1983 w/revision in 1988
Soil, climate and elevation all separate Chalk Hill from other parts of Sonoma’s
Russian River Valley. Occupying the northeast corner of the larger Russian River AVA, Chalk Hill is named for its unique, volcanically-derived, chalky white ash soils. These mildly fertile soils lend themselves to the production of excellent whites, particularly Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc. Chalk Hill’s five wineries sit above the rest of the valley, on the western benchland slopes of the Mayacamas Mountains, separating Sonoma from Napa. The appellation enjoys a warmer climate relative to the rest of the Russian River Valley. Due to the higher elevation of this viticultural area, vineyards escape much of the cooling fog that regularly shrouds the lower-lying growing areas near the river. More Info.