Appellations
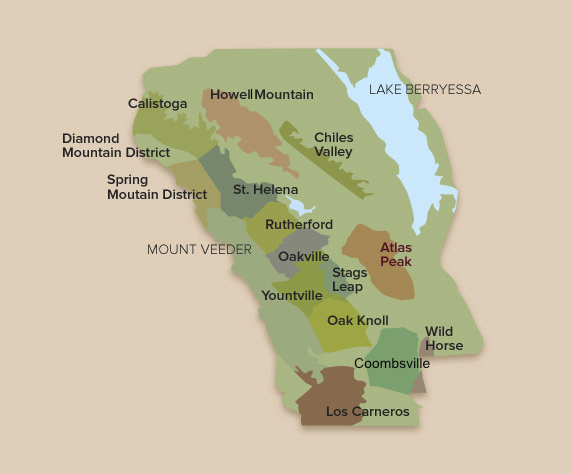
Diamond Mountain Appellation (AVA)
Diamond Mountain Climate: Moderately warm temperatures with lower maximum temperatures and higher minimum temperatures than north Napa Valley floor, due to topography and altitude. Significantly cooler than valley floor near Calistoga, 50 to 95°F in growing season (10 to 32°C).
Elevation: 400 to 2200 ft. (130 to 530m)
Rainfall: 40 to 55 inches (135cm) annually.
Soils: Residual uplifted soils of volcanic origin, often reddish and very fine-grained, even gritty in texture, composed of both weathered sedimentary and volcanic origin.
Principal varieties & characteristics in the Diamond Mountain Appellation: Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc: firmly structured, rich and fairly tannic when young, with strong blackcurrant, mineral, and cedary flavors. Less supple and fleshy than valley or benchland wines, with good aging potential. Chardonnay: Full-bodied, yet revealing mineral, green apple-peach aromas with fairly firm acidity; less richly textured than valley floor wines. More info.